105 Inch Lbs To Ft Lbs
Webtuts
May 10, 2025 · 5 min read
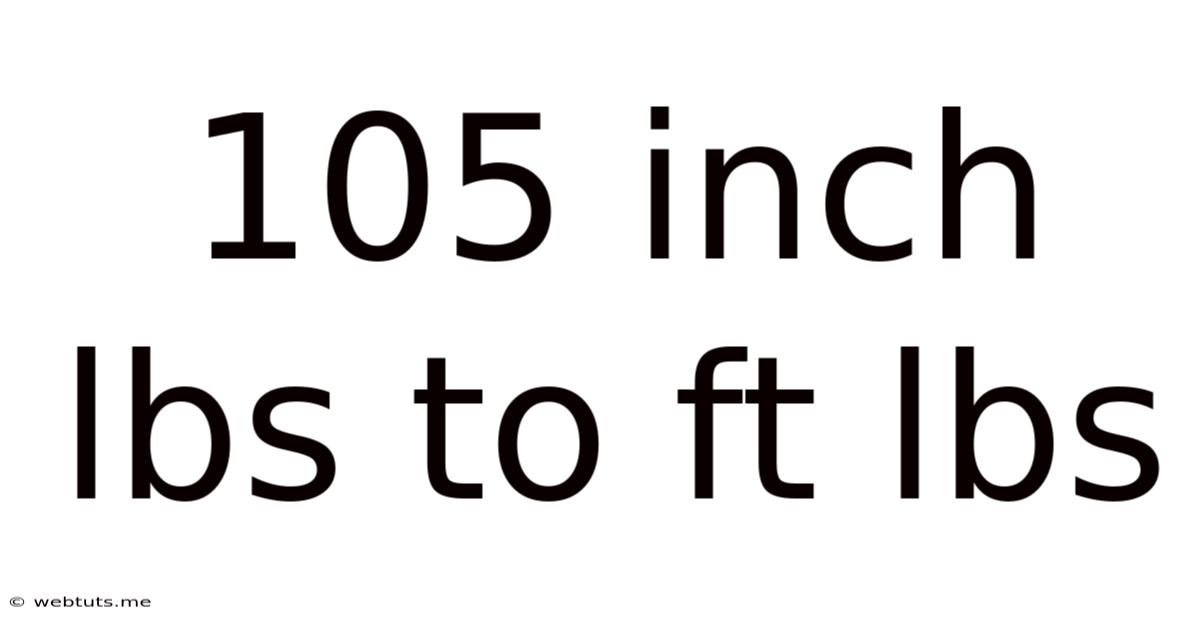
Table of Contents
105 Inch-lbs to ft-lbs: A Comprehensive Guide to Torque Conversion
Torque, a crucial concept in mechanics and engineering, represents the rotational force applied to an object. Understanding and converting torque units is essential for various applications, from tightening bolts to designing machinery. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion of 105 inch-pounds (in-lbs) to foot-pounds (ft-lbs), exploring the underlying principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Torque and its Units
Before diving into the conversion, let's solidify our grasp of torque. Torque, often denoted by the symbol τ (tau), is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. It's calculated as the product of force and the perpendicular distance from the point of application of the force to the axis of rotation. The formula is:
τ = F × r
Where:
- τ represents torque
- F represents force
- r represents the distance from the axis of rotation
The units of torque reflect this calculation. Common units include:
- Newton-meters (N⋅m): Primarily used in the International System of Units (SI).
- Foot-pounds (ft-lbs): Widely used in the United States and other countries employing the imperial system.
- Inch-pounds (in-lbs): Also common in the imperial system, often used for smaller applications.
Understanding the relationship between these units is crucial for accurate calculations and avoiding errors in engineering and mechanical applications.
Converting Inch-pounds to Foot-pounds
The conversion between inch-pounds and foot-pounds is straightforward since both units are based on the imperial system. The key is recognizing that there are 12 inches in one foot. Therefore, to convert from inch-pounds to foot-pounds, we simply divide the inch-pound value by 12.
The Conversion Formula:
ft-lbs = in-lbs / 12
Applying this formula to convert 105 inch-pounds:
ft-lbs = 105 in-lbs / 12 = 8.75 ft-lbs
Therefore, 105 inch-pounds is equal to 8.75 foot-pounds.
Practical Applications and Examples
The conversion from inch-lbs to ft-lbs finds application in numerous scenarios, both in professional and DIY settings. Let's explore some real-world examples:
1. Automotive Repair and Maintenance:
Many automotive repair manuals specify torque values in ft-lbs. If a manual calls for 8.75 ft-lbs to tighten a particular bolt, and your torque wrench only reads in in-lbs, knowing the equivalent of 105 in-lbs is vital to ensure proper tightening and prevent damage. Incorrect torque can lead to stripped threads or loose fasteners, potentially compromising the vehicle's safety and performance. Understanding this conversion helps mechanics perform accurate repairs.
2. Industrial Manufacturing:
In industrial settings, precise torque control is critical for assembling machinery and ensuring structural integrity. From constructing engines to assembling intricate electronic components, converting between inch-lbs and ft-lbs ensures accurate torque application, preventing premature wear and failure. Manufacturing processes often involve detailed specifications, making unit conversions a crucial part of quality control.
3. DIY Projects:
Even for DIY projects like assembling furniture or bicycle repairs, applying the correct torque is essential. While less critical than in professional applications, applying excessive force can damage components. Using a torque wrench and understanding the conversion from inch-lbs to ft-lbs ensures you avoid over-tightening, preserving the longevity and integrity of the assembled item.
4. Aerospace Engineering:
In the aerospace industry, precision is paramount. Miscalculations in torque can have catastrophic consequences. The conversion between inch-lbs and ft-lbs is crucial for ensuring that components are assembled correctly and that the aircraft is structurally sound.
Importance of Accurate Torque Application
Regardless of the application, applying the correct torque is crucial. Incorrect torque values can lead to a range of issues, including:
- Stripped Threads: Over-tightening can damage the threads on bolts and nuts, making them unusable.
- Broken Fasteners: Excessive torque can cause bolts, nuts, or screws to break, requiring costly replacements and repairs.
- Loose Connections: Under-tightening leads to loose connections, which can cause components to malfunction or fail.
- Safety Hazards: In many applications, proper torque is critical for safety. Improperly tightened components can lead to failures with potentially serious consequences.
Using Torque Wrenches
Accurate torque application relies heavily on using a torque wrench. Torque wrenches are tools designed to apply a precise amount of torque. They come in various types, including:
- Beam-type torque wrenches: These wrenches use a simple beam and pointer to indicate the applied torque.
- Click-type torque wrenches: These wrenches “click” when the desired torque is reached, providing a clear indication of proper tightening.
- Digital torque wrenches: These wrenches provide a digital readout of the applied torque, offering high accuracy and ease of use.
Regardless of the type, selecting an appropriate torque wrench and understanding the units is crucial for success.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Torque Considerations
While converting 105 in-lbs to ft-lbs is straightforward, advanced torque calculations often involve more complex scenarios:
- Angular Acceleration: Torque is directly related to angular acceleration. Understanding this relationship is crucial in dynamics and rotational motion problems.
- Torque Vectors: Torque is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. This becomes important when dealing with multiple torques acting on an object.
- Static vs. Dynamic Torque: Static torque is applied to a stationary object, while dynamic torque involves rotating objects. The calculations differ for these cases.
These advanced concepts are important for engineers and professionals working with complex mechanical systems.
Conclusion: Mastering Torque Conversions
Mastering the conversion of torque units, specifically from inch-pounds to foot-pounds, is a fundamental skill in various fields. The conversion of 105 in-lbs to 8.75 ft-lbs, as demonstrated, showcases the simplicity of this conversion but highlights the critical importance of accuracy. Proper torque application ensures the safety, reliability, and longevity of mechanical systems and components, impacting everything from automotive repair to aerospace engineering. Always remember to use appropriate tools, such as torque wrenches, and double-check your calculations to avoid potential problems. Thorough understanding and diligent application of these principles are crucial for success in mechanical engineering and related disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
500 Watts Is How Many Amps
May 10, 2025
-
How Many More Days Till July 10
May 10, 2025
-
How Many Days Til July 2
May 10, 2025
-
39 Miles Per Gallon To Kilometers Per Liter
May 10, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 250 Libras En Kg
May 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 105 Inch Lbs To Ft Lbs . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.