Canadian Wildfire Smoke Chokes Nebraska Air
Webtuts
Jun 09, 2025 · 7 min read
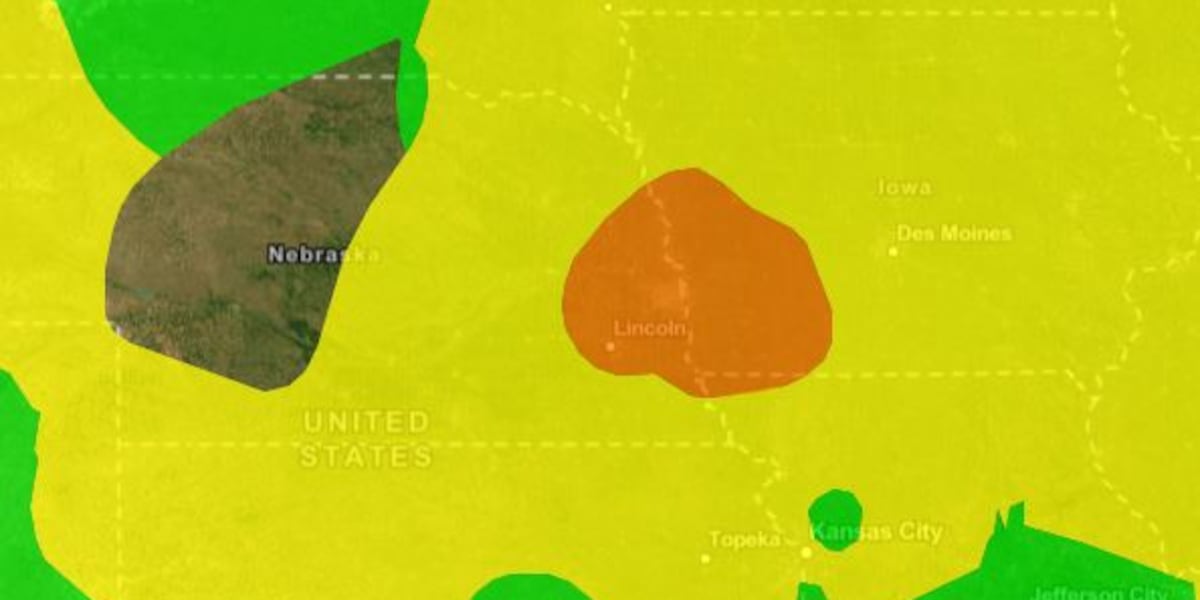
Table of Contents
Canadian Wildfire Smoke Chokes Nebraska Air: A Deep Dive into the 2023 Crisis and Beyond
The summer of 2023 witnessed a devastating confluence of events, primarily the unprecedented scale of Canadian wildfires, which sent plumes of thick, hazardous smoke billowing southwards, impacting air quality across vast swathes of the United States, including Nebraska. This wasn't just a fleeting inconvenience; the smoke caused significant health concerns, economic disruption, and raised crucial questions about climate change, forest management, and transboundary air pollution. This article will delve into the specifics of the 2023 crisis, exploring the science behind the smoke's journey, its impact on Nebraska, and the broader implications for the future.
The Unfolding Disaster: How Canadian Wildfires Impacted Nebraska
The 2023 wildfire season in Canada was unlike any before. Millions of acres burned, fueled by an unusually dry and warm spring followed by a prolonged heatwave. The sheer scale of these fires, particularly in provinces like Quebec, Ontario, and British Columbia, generated an unprecedented amount of smoke. Meteorological conditions played a crucial role. Specific atmospheric patterns, including high-pressure systems and prevailing winds, acted as a conduit, transporting the smoke hundreds, even thousands, of miles south into the United States. Nebraska, lying directly in the path of these prevailing winds, experienced some of the worst air quality in the country for extended periods.
-
The Journey of the Smoke: The smoke didn't arrive as a single, massive plume. Instead, it arrived in waves, often coinciding with shifts in wind direction and atmospheric pressure. Satellite imagery and air quality monitoring networks tracked these movements, showing the smoke’s progression from Canada, across the Great Lakes region, and finally impacting Nebraska. The smoke’s journey wasn't a straight line; it dispersed, concentrated, and shifted depending on weather patterns.
-
Impact on Nebraska's Air Quality: The air quality index (AQI) in Nebraska soared into the unhealthy and hazardous ranges for days, sometimes weeks. This meant significantly elevated levels of particulate matter (PM2.5), tiny particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs and cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular issues, and other health complications. Areas in eastern and central Nebraska were particularly affected, with many cities reporting AQI values well above recommended safe levels.
-
Visibility Reduction: The smoke wasn't just unhealthy; it also dramatically reduced visibility. Driving conditions became hazardous, particularly on highways and rural roads. Airports experienced flight delays and cancellations as pilots navigated reduced visibility. Many outdoor activities were cancelled or postponed, impacting recreational and economic sectors.
-
Health Impacts: The health consequences were significant. Hospitals reported an increase in respiratory illnesses, asthma attacks, and other ailments related to poor air quality. Vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, were at particularly high risk. Public health officials issued warnings urging residents to stay indoors, limit strenuous outdoor activities, and take other precautions.
The Science Behind the Smoke: Particulate Matter and its Effects
The primary culprit behind the health concerns associated with wildfire smoke is particulate matter, specifically PM2.5. These are fine particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or less – about 3% the width of a human hair. Their small size allows them to bypass the body's natural defenses and penetrate deep into the lungs and even the bloodstream.
-
Composition of Wildfire Smoke: Wildfire smoke is a complex mixture of various pollutants, including PM2.5, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and hazardous air pollutants. The specific composition varies depending on the type of vegetation burning and the intensity of the fire. However, PM2.5 is generally the dominant pollutant responsible for the most significant health impacts.
-
PM2.5 and Respiratory Problems: Inhaling PM2.5 can trigger inflammation in the lungs, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing, and other respiratory symptoms. Long-term exposure is linked to more serious conditions like chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer.
-
PM2.5 and Cardiovascular Issues: Studies have demonstrated a strong link between PM2.5 exposure and cardiovascular problems. The tiny particles can enter the bloodstream, contributing to inflammation and blood clotting, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
-
Other Health Effects: Besides respiratory and cardiovascular effects, PM2.5 exposure is associated with various other health problems, including eye irritation, neurological effects, and reduced lung function. Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable due to their developing or compromised respiratory systems.
Beyond the Immediate Crisis: Long-Term Impacts and Future Preparedness
The 2023 Canadian wildfire smoke event was a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of environmental challenges. It highlighted the need for a multi-faceted approach to address the problem, going beyond immediate crisis response.
-
Climate Change and Wildfires: Climate change is widely recognized as a major driver of increased wildfire frequency, intensity, and duration. Warmer temperatures, prolonged droughts, and changes in precipitation patterns create conditions ripe for devastating wildfires. Addressing climate change through emission reductions is crucial to mitigating the risk of future events.
-
Forest Management Practices: Sustainable forest management practices are essential in reducing the risk of large-scale wildfires. This includes controlled burns, forest thinning, and proactive measures to reduce the accumulation of flammable material. Improved forest health can reduce the severity and spread of wildfires.
-
Transboundary Air Pollution: The Canadian wildfire smoke crisis highlighted the transboundary nature of air pollution. Air pollution doesn't respect national borders, emphasizing the need for international cooperation and information sharing to monitor and manage air quality across regions.
-
Public Health Preparedness: Effective public health infrastructure is critical in mitigating the health consequences of wildfire smoke. This includes air quality monitoring networks, early warning systems, public health advisories, and access to healthcare for vulnerable populations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can I protect myself from wildfire smoke?
A1: When air quality is poor, stay indoors as much as possible. Use air purifiers with HEPA filters to remove particulate matter from the air. Limit strenuous outdoor activities. Keep windows and doors closed, and run air conditioning with the air recirculation option on. Consult your doctor if you have respiratory problems or other health concerns.
Q2: How long will the smoke last?
A2: The duration of smoke events is highly variable and dependent on weather patterns and the ongoing activity of the wildfires. It can range from a few days to several weeks. Monitoring air quality reports and weather forecasts is crucial for staying informed.
Q3: What are the economic impacts of wildfire smoke?
A3: The economic impacts can be significant, including reduced tourism, decreased agricultural yields, increased healthcare costs, and lost productivity due to reduced visibility and health concerns. The disruption of transportation and supply chains can also lead to considerable economic losses.
Q4: What is the government doing to address the issue?
A4: Governments at all levels are implementing various strategies, including enhancing wildfire prevention and suppression efforts, improving air quality monitoring systems, developing public health campaigns to raise awareness about the health risks of wildfire smoke, and supporting research on wildfire mitigation and climate change adaptation. International cooperation is also crucial in addressing transboundary air pollution issues.
Q5: Can we prevent future events like this?
A5: While completely preventing future wildfire smoke events is unlikely, proactive measures can significantly reduce their frequency, intensity, and impact. Addressing climate change, implementing effective forest management practices, and improving public health preparedness are all crucial steps in mitigating the risks.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The 2023 Canadian wildfire smoke crisis had a profound impact on Nebraska, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of environmental challenges. The event served as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of climate change, forest management, public health, and international cooperation. Moving forward, a multi-faceted approach involving emission reductions, improved forest management, robust public health infrastructure, and international collaboration is crucial to mitigate the risks of future events and protect the health and well-being of communities across North America. For more information on air quality monitoring, wildfire prevention, and public health resources, please visit [insert relevant links to government websites and resources here]. Stay informed and take proactive steps to protect yourself and your family.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Love Vs Rodgers Jersey Swap On The Horizon
Jun 09, 2025
-
Former Lions Safety Eagles Disrespect
Jun 09, 2025
-
June 11th Full Moon A Powerful Time For 3 Zodiac Signs
Jun 09, 2025
-
Canadian Army Assists Ontario Wildfire Fight
Jun 09, 2025
-
Packers Fans Predict 11 Wins In 2025
Jun 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Canadian Wildfire Smoke Chokes Nebraska Air . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.