Colombia Earthquake: 6.3 Magnitude Strikes
Webtuts
Jun 08, 2025 · 7 min read
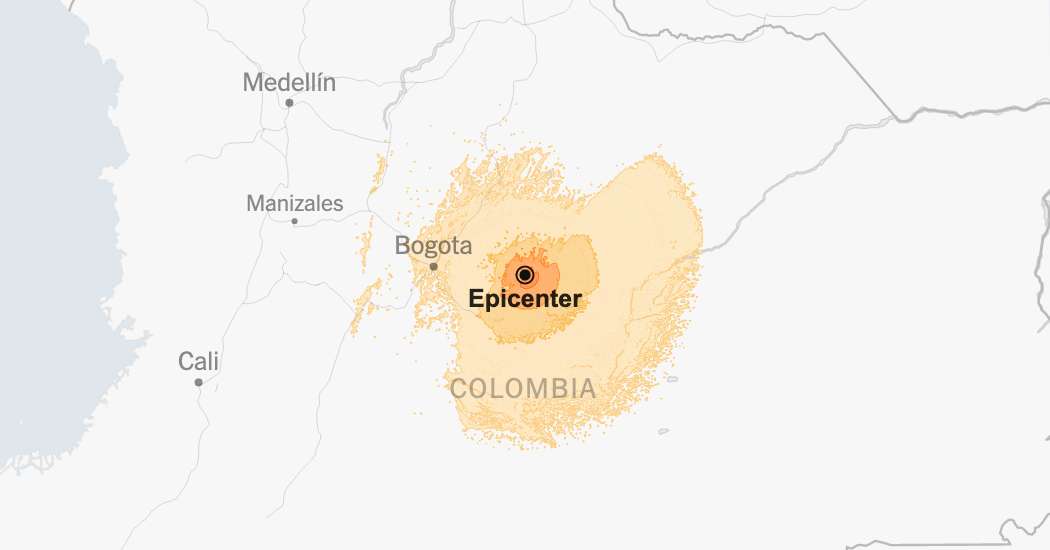
Table of Contents
Colombia Earthquake: 6.3 Magnitude Strikes – A Comprehensive Overview
Colombia, a nation nestled along the volatile Ring of Fire, experienced a significant earthquake on [Insert Date of Earthquake]. The 6.3 magnitude tremor, centered near [Insert precise location and proximity to major cities], sent shockwaves across the country, triggering widespread panic and leaving a trail of destruction in its wake. This article delves into the details of this seismic event, exploring its geological underpinnings, the immediate impact, the ongoing recovery efforts, and the broader implications for earthquake preparedness in the region. Understanding the complexities of this earthquake is crucial not only for comprehending the immediate aftermath but also for improving future disaster response and mitigation strategies. This event serves as a stark reminder of the potent forces at play beneath the Earth's surface and the importance of proactive measures to protect lives and infrastructure.
Understanding the Geological Context of the Earthquake
The earthquake's occurrence is intrinsically linked to Colombia's precarious geological position. The country sits at the juncture of several tectonic plates, primarily the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate. The Nazca Plate, denser and heavier, is subducting (sliding beneath) the South American Plate. This constant movement, characterized by immense pressure and friction, generates significant stress along the subduction zone. Over time, this stress accumulates until it surpasses the strength of the rocks, resulting in a sudden release of energy – an earthquake.
-
The Focal Depth: The depth of the earthquake's focus (hypocenter) is a critical factor in determining its intensity at the surface. A shallower earthquake, closer to the surface, generally causes more severe ground shaking and damage than a deeper one. [Insert information on the focal depth of the earthquake and its implications].
-
Fault Line Involvement: Precise identification of the specific fault line responsible for the earthquake is crucial for understanding its mechanism and predicting potential aftershocks. [Insert details about the specific fault line involved, if known, and its geological history].
-
Seismic Waves: The energy released during the earthquake propagates outwards in the form of seismic waves – P-waves (primary waves), S-waves (secondary waves), and surface waves. These waves travel at different speeds and cause different types of ground motion. P-waves are the fastest and arrive first, followed by S-waves, which cause more significant shaking. Surface waves, traveling along the Earth's surface, are responsible for the most destructive effects.
The Immediate Impact: Destruction and Casualties
The 6.3 magnitude earthquake caused significant damage across [mention specific affected areas]. Initial reports indicated [Insert details on casualties – number of deaths and injuries]. The extent of the damage varied considerably depending on factors such as the distance from the epicenter, the quality of building construction, and the type of soil.
-
Building Collapse: Older buildings, particularly those lacking modern earthquake-resistant design features, suffered the most significant damage, with many collapsing completely or sustaining severe structural damage. [Include specific examples of collapsed buildings or types of structures most affected].
-
Infrastructure Damage: The earthquake also impacted crucial infrastructure, including roads, bridges, power lines, and water supply systems. Disruptions to these systems exacerbated the challenges faced by rescue and relief efforts. [Provide details on specific infrastructure damage and its consequences].
-
Landslides and Ground Ruptures: The intense shaking triggered landslides in mountainous regions, further obstructing rescue efforts and adding to the devastation. Ground ruptures, where the Earth's surface cracks and shifts, also contributed to the damage. [Include specific information on landslides or ground ruptures if available].
-
Psychological Trauma: Beyond the physical devastation, the earthquake caused widespread psychological trauma among the affected population. The sudden and violent shaking, the loss of loved ones, and the destruction of homes and belongings left many people in a state of shock and despair. [Discuss the mental health implications and efforts to provide support].
Rescue and Relief Efforts: A Collaborative Response
The immediate aftermath of the earthquake saw a swift and coordinated response from various agencies. [Insert details about the organizations involved in rescue and relief – government agencies, international organizations, NGOs, etc.].
-
Search and Rescue Operations: Rescue teams, equipped with specialized equipment, worked tirelessly to locate and extract survivors from collapsed buildings. [Include details about the rescue techniques employed and challenges faced].
-
Medical Assistance: Medical teams provided essential medical care to the injured, establishing temporary medical facilities to cope with the influx of casualties. [Include information on the provision of medical supplies and treatment].
-
Shelter and Food Distribution: Organizations provided shelter, food, water, and other essential supplies to those displaced by the earthquake. [Mention the logistical challenges and the methods used to distribute aid].
-
International Aid: International aid organizations played a significant role in supporting the relief efforts, providing financial assistance, supplies, and expertise. [Include details about international assistance received].
The Long Road to Recovery: Reconstruction and Mitigation
The recovery from the earthquake will be a long and complex process. Beyond the immediate relief efforts, long-term reconstruction and mitigation strategies are vital to build resilience and prevent future tragedies.
-
Reconstruction of Infrastructure: Rebuilding damaged infrastructure, including homes, schools, hospitals, and transportation networks, is a substantial undertaking requiring significant resources and careful planning. [Discuss the challenges and strategies for reconstruction].
-
Building Codes and Earthquake-Resistant Design: Strengthening building codes and implementing earthquake-resistant design standards in new constructions are crucial to reducing vulnerability to future seismic events. [Highlight the importance of updated building regulations].
-
Early Warning Systems: Investing in and improving early warning systems can provide valuable time for people to evacuate and take protective measures before a major earthquake strikes. [Discuss existing systems and potential improvements].
-
Community Preparedness: Educating communities about earthquake preparedness, including what to do before, during, and after an earthquake, is crucial in minimizing casualties and damage. [Highlight the role of public awareness campaigns].
Scientific Insights and Future Predictions
The 6.3 magnitude earthquake in Colombia provides valuable data for seismologists and geologists to refine their understanding of seismic activity in the region.
-
Seismic Monitoring: Detailed analysis of seismic data from the earthquake and its aftershocks can improve the accuracy of earthquake hazard assessments and help predict future seismic events. [Discuss the importance of ongoing seismic monitoring].
-
Geological Mapping: Detailed geological mapping of the affected area can help identify fault lines and other geological features that pose a seismic risk. [Highlight the value of geological surveys].
-
Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Combining scientific data with detailed risk assessments can inform the development of effective mitigation strategies to minimize the impact of future earthquakes. [Discuss the importance of integrating scientific knowledge into disaster management].
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What caused the Colombia earthquake?
A1: The earthquake was caused by the movement of tectonic plates, specifically the subduction of the Nazca Plate beneath the South American Plate. This movement builds up stress, which is released suddenly in the form of an earthquake.
Q2: How strong was the earthquake?
A2: The earthquake had a magnitude of 6.3 on the moment magnitude scale.
Q3: Where was the epicenter of the earthquake?
A3: The epicenter was located near [Insert precise location].
Q4: What kind of damage did the earthquake cause?
A4: The earthquake caused significant damage to buildings, infrastructure, and triggered landslides. There were casualties reported.
Q5: What is being done to help the affected areas?
A5: Extensive rescue and relief efforts are underway, involving government agencies, international organizations, and NGOs. Reconstruction efforts are also planned.
Q6: How can I help the victims of the earthquake?
A6: You can donate to reputable charitable organizations involved in the relief and recovery efforts.
Conclusion and Call to Action
The 6.3 magnitude earthquake in Colombia serves as a poignant reminder of the power of nature and the vulnerability of human settlements in seismically active regions. The immediate aftermath highlights the importance of robust disaster preparedness and response mechanisms. Moving forward, significant investments in infrastructure improvements, building codes, early warning systems, and public awareness campaigns are crucial to mitigate future risks and build more resilient communities. To learn more about earthquake preparedness and global seismic activity, explore our other articles on [Link to other relevant articles]. Your awareness and preparedness can make a difference.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowcountry Thunderstorm Watch Cancelled
Jun 09, 2025
-
Dallas Derecho Warning 90mph Winds Hail Sunday
Jun 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Colombia Earthquake: 6.3 Magnitude Strikes . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.