How Many Amps Is 1500 Watts At 120 Volts
Webtuts
May 09, 2025 · 4 min read
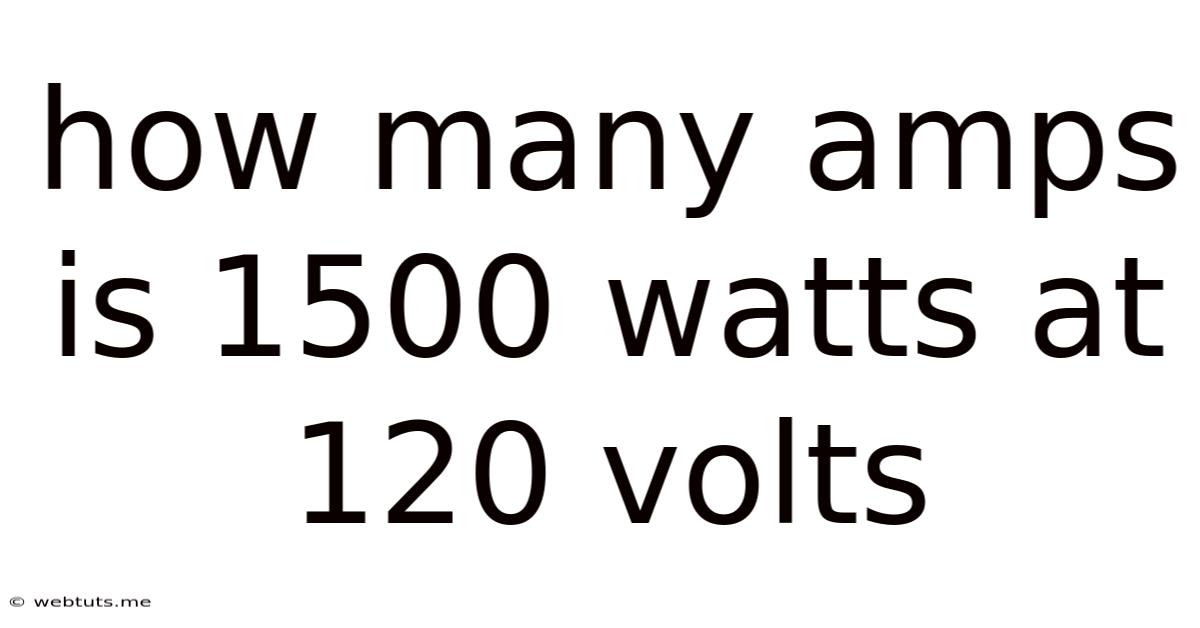
Table of Contents
How Many Amps is 1500 Watts at 120 Volts? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between watts, volts, and amps is crucial for anyone working with electricity. This is especially important for ensuring the safety and proper functioning of electrical devices and avoiding potential hazards. This article will delve deep into the calculation of amperage (amps) from wattage and voltage, focusing specifically on the question: how many amps is 1500 watts at 120 volts? We’ll cover the underlying formula, practical applications, safety considerations, and even explore scenarios involving different voltage levels.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Watts, Volts, and Amps
Before diving into the specific calculation, let's solidify our understanding of the three fundamental electrical units:
-
Watts (W): This unit measures power, representing the rate at which energy is consumed or produced. A higher wattage indicates a higher rate of energy consumption. Think of it as the "strength" of the electrical flow.
-
Volts (V): This unit measures electrical potential difference or voltage. It's the "pressure" that pushes electrons through a circuit. A higher voltage means a greater electrical pressure.
-
Amps (A): This unit measures electrical current, representing the flow of electrons through a circuit. It's the "amount" of electrical flow. A higher amperage indicates a larger flow of electrons.
These three units are interconnected through a simple yet powerful formula:
Power (Watts) = Voltage (Volts) x Current (Amps)
Or, more concisely: P = V x I
Calculating Amps from Watts and Volts
To determine the amperage (I) for a 1500-watt device operating at 120 volts, we can rearrange the formula above:
I = P / V
Plugging in the values:
I = 1500 W / 120 V = 12.5 A
Therefore, a 1500-watt device operating at 120 volts draws 12.5 amps.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Understanding this calculation has numerous practical applications:
-
Circuit Breaker Sizing: Knowing the amperage draw is crucial for selecting the appropriate circuit breaker for a specific appliance. A 1500-watt device at 120V requires a circuit breaker rated for at least 15 amps (it's always best to have some headroom to account for surges). Using a smaller breaker could lead to overheating and potential fire hazards.
-
Extension Cord Selection: Extension cords have current ratings. Using an extension cord with a lower amp rating than the device's draw can result in overheating, melting, and fire hazards. Always use a cord with an amp rating sufficient for the load.
-
Power Supply Design: For electronics designers, understanding the relationship between watts, volts, and amps is critical for designing power supplies capable of meeting the demands of a circuit. Undersized power supplies can lead to malfunction or damage.
-
Energy Consumption: Monitoring the amperage draw helps you estimate the energy consumption of a device. This is valuable for calculating energy costs and identifying potential energy-saving opportunities.
Safety Precautions: Avoiding Overloads and Hazards
Working with electricity demands utmost caution. Here are some vital safety considerations:
-
Never exceed the rated amperage of any electrical component. Overloading circuits leads to overheating, fire hazards, and potential injury.
-
Always use properly grounded electrical outlets. Grounding provides a path for fault currents to flow safely to the earth, preventing electric shock.
-
Inspect electrical cords and appliances regularly for signs of damage. Damaged cords or appliances should be immediately replaced.
-
If you are not comfortable working with electricity, consult a qualified electrician. Improper handling of electrical systems can result in severe injury or even death.
Scenarios with Different Voltages
While our primary focus is on 120 volts, it's important to note that the calculation changes with different voltage levels. For example:
-
240 Volts: If the same 1500-watt device were operating at 240 volts, the amperage would be:
I = 1500 W / 240 V = 6.25 A
Notice that the amperage is significantly lower at a higher voltage. This is because a higher voltage requires less current to deliver the same power.
Advanced Considerations: Power Factor
In AC circuits, the power factor comes into play. The power factor represents the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt-amps). A power factor less than 1 indicates that some of the current is not contributing to the actual work done. In such cases, the calculation becomes slightly more complex:
I = P / (V x Power Factor)
For purely resistive loads (like incandescent light bulbs), the power factor is 1. However, for inductive loads (like motors), the power factor can be significantly less than 1. This is why it is important to consider the power factor when dealing with motors and other inductive devices.
Conclusion: Mastering Watts, Volts, and Amps
The relationship between watts, volts, and amps is a cornerstone of electrical understanding. Mastering this relationship is not just about performing calculations; it's about ensuring electrical safety, designing efficient systems, and making informed decisions regarding electrical equipment. By carefully considering the amperage draw of appliances and adhering to safety guidelines, you can minimize risks and optimize your electrical usage. Remember that understanding the intricacies of electrical circuits is crucial for safe and efficient electrical work. Always prioritize safety when dealing with electricity and seek professional help if you are unsure about any aspect of electrical work. This comprehensive guide provides a solid foundation for understanding the interplay of watts, volts, and amps, empowering you to handle electrical situations with confidence and safety.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Ounces Is Three Liters
May 10, 2025
-
What Is 90 Degrees F In C
May 10, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 3 In Oz
May 10, 2025
-
What Is 6 5 As A Fraction
May 10, 2025
-
How Many Teaspoons Are In 4 Ounces
May 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Amps Is 1500 Watts At 120 Volts . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.