What Is 72 Degrees F In Celsius
Webtuts
May 12, 2025 · 5 min read
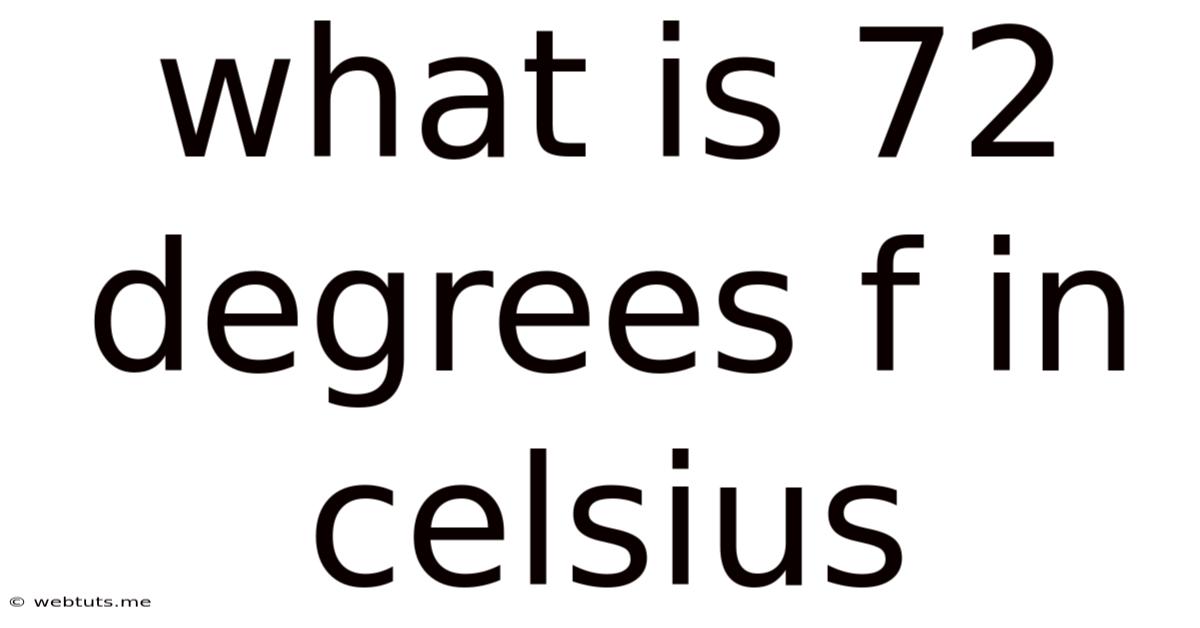
Table of Contents
What is 72 Degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide
Knowing how to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is a crucial skill, especially in our increasingly globalized world. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "What is 72 degrees Fahrenheit in Celsius?" but also delve into the intricacies of temperature conversion, explore the history of both scales, and provide practical applications for this knowledge.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before we dive into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two temperature scales involved:
Fahrenheit (°F)
The Fahrenheit scale, named after German-Dutch physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, is a temperature scale where the freezing point of water is 32 degrees (°F) and the boiling point is 212 °F at one atmosphere of pressure. It's primarily used in the United States, a few Caribbean nations, and some parts of the Pacific.
Celsius (°C)
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. On this scale, the freezing point of water is 0 °C and the boiling point is 100 °C at one atmosphere of pressure. It's the most widely used temperature scale globally, adopted by the International System of Units (SI) and favored in scientific contexts.
Converting 72°F to Celsius
The formula for converting Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C) is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 72°F:
°C = (72 - 32) × 5/9 = 40 × 5/9 = 22.22°C (approximately)
Therefore, 72 degrees Fahrenheit is approximately 22.22 degrees Celsius.
Beyond the Conversion: A Deeper Dive into Temperature
Understanding temperature conversion goes beyond simply plugging numbers into a formula. It involves grasping the fundamental principles of heat and its measurement.
Heat vs. Temperature
While often used interchangeably, heat and temperature are distinct concepts. Heat is the total energy of molecular motion in a substance, while temperature measures the average kinetic energy of the molecules. A large object can have more heat than a small object at the same temperature because it contains more molecules.
Absolute Zero
Both Fahrenheit and Celsius scales are relative scales, meaning their zero points are arbitrarily defined. However, there's an absolute temperature scale called the Kelvin scale (K). Kelvin's zero point represents absolute zero, the theoretical temperature at which all molecular motion ceases. This is -273.15 °C or -459.67 °F. The Kelvin scale is crucial in scientific calculations and thermodynamics.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
Understanding temperature is crucial because of its impact on the physical properties of matter. Most substances expand when heated and contract when cooled. This principle is applied in various technologies, from thermometers to bimetallic strips used in thermostats.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversion
The ability to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential in numerous fields:
- International Collaboration: Scientists, engineers, and businesses across the globe need a common language for temperature measurements.
- Cooking and Baking: Recipes often specify temperatures in either Fahrenheit or Celsius. Accurate conversion ensures consistent results.
- Medicine: Accurate body temperature measurement and monitoring require proficiency in temperature conversion.
- Climate and Meteorology: Weather reports often provide temperature data in both scales, catering to a diverse audience.
- Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes rely on precise temperature control, necessitating accurate conversion for monitoring and regulation.
The History of Temperature Scales: A Journey Through Time
Understanding the history of Fahrenheit and Celsius adds another layer of appreciation to their significance.
The Development of Fahrenheit
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit developed his scale around 1724. His original scale used several reference points, including the freezing point of a water-ice-salt mixture (0 °F) and human body temperature (around 96 °F). These reference points have been refined over time, leading to the current standard.
The Development of Celsius
Anders Celsius proposed his scale in 1742, initially defining 0 °C as the boiling point of water and 100 °C as the freezing point. This was later reversed to the current convention, with 0 °C representing the freezing point and 100 °C the boiling point of water at sea level.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Temperature Concepts
For those seeking a deeper understanding, here are some advanced concepts related to temperature:
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is the movement of thermal energy from a hotter object to a cooler object. There are three primary modes of heat transfer: conduction (through direct contact), convection (through fluid movement), and radiation (through electromagnetic waves).
Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one unit mass of a substance by one degree Celsius (or one Kelvin). Different materials have different specific heat capacities. Water, for example, has a relatively high specific heat capacity, meaning it takes a lot of heat to raise its temperature.
Thermal Equilibrium
Thermal equilibrium is the state where two or more objects in thermal contact have reached the same temperature and no further net heat transfer occurs.
Entropy
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness of a system. The second law of thermodynamics states that the total entropy of an isolated system can only increase over time.
Tips and Tricks for Temperature Conversion
While the formula is straightforward, here are some tips for accurate and efficient temperature conversion:
- Use a calculator: A calculator ensures accuracy, especially when dealing with decimal places.
- Double-check your work: After converting, double-check your answer to avoid errors.
- Memorize the key conversion points: Knowing that 0°C is 32°F and 100°C is 212°F can help estimate conversions quickly.
- Utilize online converters: Many free online converters are available for quick and easy temperature conversions.
Conclusion: Mastering Temperature Conversion for a Connected World
Understanding temperature conversion, especially between Fahrenheit and Celsius, is crucial for effective communication and problem-solving in various aspects of life. From everyday tasks to scientific research, the ability to seamlessly convert between these scales ensures clarity and accuracy. While this guide provides a comprehensive overview, continuous learning and exploration of related concepts will further enhance your understanding of this essential skill. Remember that mastering temperature conversion is not just about the formula; it's about understanding the underlying principles of heat, temperature, and their profound impact on our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Calculate Raise In Pay
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Square Yards Is A 12x12 Room
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Days Till The 27
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Days Has It Been Since July 5
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 185 Mm
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 72 Degrees F In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.